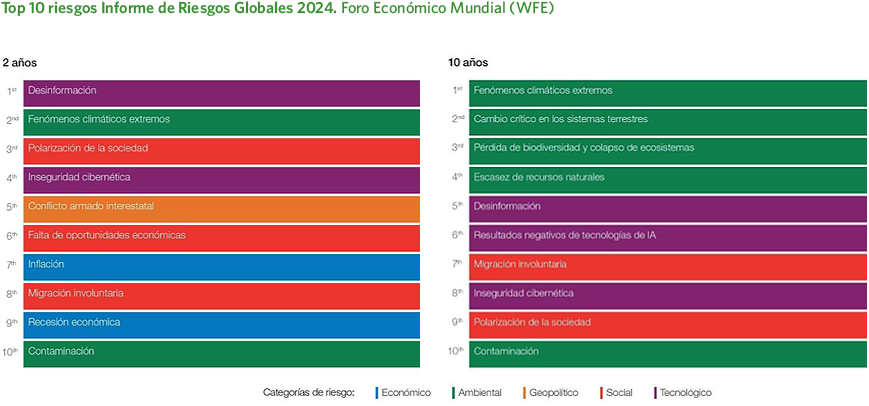
The Global Risks Report 2024 from the World Economic Forum (WEF) highlights the growing complexity and interconnection among the major risks facing the world in both the short and long term. In the short term, dominant threats include AI-driven misinformation, extreme weather events, social polarization, the cost-of-living crisis, and cyberattacks. In the long term, risks intensify around climate change, with severe climate events, ecosystem disruption, biodiversity loss, and scarcity of natural resources emerging as critical threats.
Madrileña Red de Gas manages its risks in an integrated, systematic, and anticipatory manner, incorporating risk management into its corporate strategy and daily decision-making processes
Madrileña Red de Gas manages its risks in an integrated, systematic, and anticipatory manner, incorporating risk management into its corporate strategy and daily decision-making processes. To achieve this, the company identifies, assesses, and prioritizes potential risks—whether financial, operational, climate-related, technological, reputational, or regulatory—and designs action plans to prevent, mitigate, or adapt to their impacts.
For each organizational objective, the most relevant risks that could hinder its achievement are determined. Each risk is analyzed in terms of the likelihood of occurrence and overall impact, including both economic and reputational effects.
As mentioned in Chapter 3, the Audit and Risk Committee reports directly to the Board of Directors and operates in accordance with its internal regulations, which define its objectives, functions, and structure. The committee is composed of representatives from the Board of Directors of each of the four shareholders, members of the Executive Committee, and the risk management department team.
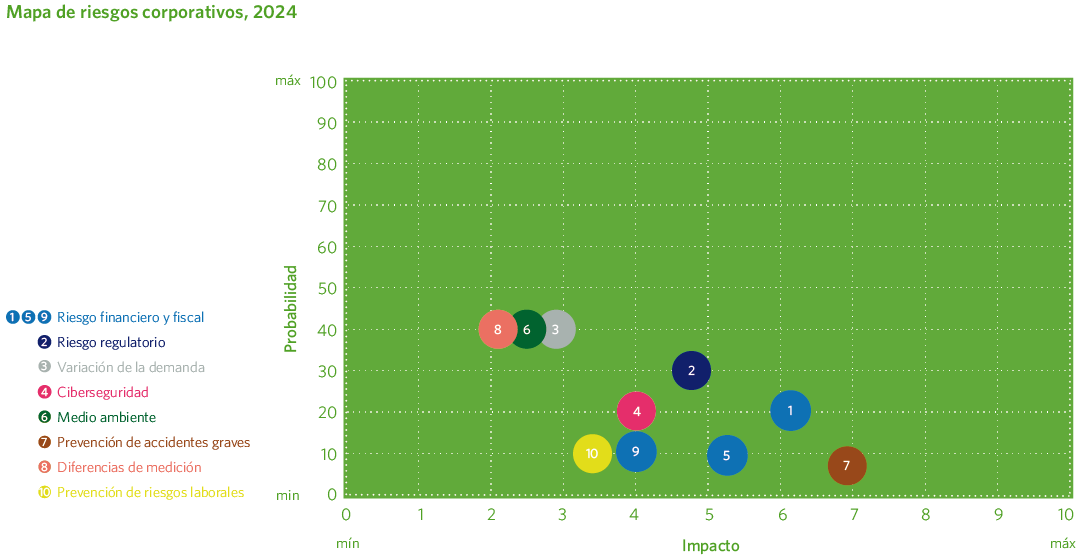
Madrileña Red de Gas corporate risks map covers a wide range of risks, with a priority focus on the ten most relevant ones, which may pose a significant threat to the achievement of its objectives or to its reputation.
The assessment of these risks has been carried out using an approach based on two main criteria:
- The probability of occurrence of each risk.
- The impact resulting from the combination of the effect on the net present value and the reputational impact. The effect on the net present value includes both the projected direct economic impact over a twenty-year period and any potential associated penalties.
The map includes emerging risks through periodic updates of its contents. In addition, it establishes new high-level controls that complement those already in place. The implemented action plans help mitigate the consequences of these risks.
Compared to previous years, in 2024 the definition and evaluation of several risks have been refined through more detailed analyses of their contextual conditions and the potential consequences that could arise if they materialize. At the same time, a strategy has been developed in parallel to prevent and mitigate the potential impacts associated with these risks.
5.1Legal and regulatory risk
Regulated Activity
The activity of natural gas distribution in Spain is a regulated activity, meaning it is subject to regulation by the State to ensure a safe, efficient, and non-discriminatory supply.
Distribution is remunerated through a regulated compensation system, which recognizes the costs of investment, operation, and maintenance associated with the assets put into service. This compensation is calculated annually by the National Commission of Markets and Competition (CNMC) according to methodologies established in sector regulations.
Access tariffs to distribution networks, known as tolls, are also set by the regulator and must be paid by all users regardless of the contracted supplier.Therefore, one of the main risks Madrileña Red de Gas faces is coping with continuous legislative changes, market restrictions, and modifications to the distribution model.
In this regard, Madrileña Red de Gas continuously and thoroughly monitors publications issued by the CNMC, adapting to new requirements and/or regulatory changes established.
Decarbonization and energy transition policies
The common goal of the European Union and its member states is to achieve full decarbonization of the economy by 2050, representing one of the greatest challenges, and at the same time opportunities, for structural transformation at the continental level. This commitment is framed within the European Green Deal, which establishes a roadmap to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent, implying a drastic reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the promotion of a sustainable and inclusive development model.
In this context, both the European Commission and national governments, including Spain’s, are adopting increasingly ambitious regulatory measures. These actions range from implementing binding regulations on energy efficiency, renewable energies, and sustainable mobility, to green fiscal reforms, economic incentives for innovation and digitalization of the energy system, and progressive restrictions on high environmental impact activities.
Gas package
Among the legislative initiatives presented by the European Commission, the so-called “Gas Package” (also known as the Hydrogen and Decarbonised Gas Market Package) stands out. In May 2024, the Council of the European Union adopted both Regulation (EU) 2024/1789 and Directive (EU) 2024/1788, which establish common rules for the internal markets of renewable gas, natural gas, and hydrogen.
This set of proposals forms an integral part of the review process of the European energy market and aims to lay the foundations for the progressive decarbonization of the gas system, adapting it to new climate and technological challenges.
In May 2024, the Council of the European Union adopted both Regulation (EU) 2024/1789 and Directive (EU) 2024/1788, which establish common rules for the internal markets of renewable gas, natural gas, and hydrogen
The main objectives of the Gas Package are:
- To facilitate the integration of renewable hydrogen and other low-carbon gases into existing infrastructures, enabling a gradual transition from natural gas to cleaner energies.
- To reform the design of the gas market to make it more flexible, competitive, and compatible with climate goals. This includes non-discriminatory network access rules, transparent tariffs, and fair conditions for new market players.
- To protect consumers and ensure a just transition, with special attention to vulnerable households and the social impacts of the energy model shift.
In Spain, this European package also implies a profound transformation of the role of gas in the economy. Although it currently remains an important source for electricity generation and industrial supply, national strategies — such as the Integrated National Energy and Climate Plan (PNIEC) — contemplate a gradual reduction in the use of fossil gas, favoring technologies such as biomethane, green hydrogen, and electrification.
Madrileña Red de Gas is working to align itself with the new EU gas regulatory framework. This includes projects to adapt its networks to cleaner energies such as hydrogen and biomethane, modernization of its systems with digital tools, and collaboration with the public sector in initiatives funded by European funds to promote the energy transition, as detailed in section 5.2 Adaptation to Climate, Resilience, and Transition of this report.
Methane emissions
Another regulatory change significantly affecting Madrileña Red de Gas is Regulation (EU) 2024/1787, approved in June 2024, concerning the reduction of methane emissions in the energy sector, which amends Regulation (EU) 2019/942.
This new regulation establishes measures to reduce methane emissions in the European Union’s energy sector, covering activities such as oil and gas production, natural gas transportation, and coal mining. It requires companies to measure and report methane emissions, conduct periodic Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) campaigns, and comply with verification standards. The goal is to improve the accuracy of emission inventories, ensure transparency, and significantly reduce methane emissions in alignment with the EU’s climate objectives.
Given the risk posed by this regulatory change, Madrileña Red de Gas has assessed its potential economic impact through pilot projects aimed at identifying gas leaks. Additionally, during this fiscal year, and pending its transposition into Spanish law, meetings have been held with groups of European distributors to harmonize criteria for the upcoming mandatory reporting requirements.
Madrileña Red de Gas has been actively working for several years on reducing such emissions through voluntary participation in the United Nations’ OGMP 2.0 program, which aims to reduce methane emissions, as detailed in section 5.2 Adaptation to Climate, Resilience, and Transition. In fact, the OGMP 2.0 project has served as a framework for the European Commission in the drafting of Regulation (EU) 2024/1787 mentioned above.
Reporting
Regarding sustainability information reporting, another regulatory challenge faced by Madrileña Red de Gas is the corporate sustainability reporting framework established by Directive 2022/2464 (known as the CSRD Directive). This new European legislation, which came into effect on January 6, 2023, aims to standardize the sustainability information disclosed by companies.
The reporting requirements set forth by the Directive will apply to Madrileña Red de Gas starting in 2026, when it publishes its Sustainability Report corresponding to the year 2025.
Throughout 2024, Madrileña Red de Gas has focused its efforts on adapting its sustainability processes to meet the CSRD requirements
Throughout 2024, Madrileña Red de Gas has focused its efforts on adapting its sustainability processes to meet the CSRD requirements, particularly through a gap analysis of the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the incorporation of the double materiality concept (financial materiality and impact materiality), as discussed in section 4.1 ESG Strategy.
However, Madrileña Red de Gas is currently awaiting the final approval of the Omnibus legislative package, whose content will be key in determining how the CSRD requirements are transposed and applied in Spain. This regulation could introduce significant adjustments to sustainability reporting criteria, especially concerning the scope of obligations, potentially removing the legal requirement for the company.
For this reason, Madrileña Red de Gas is closely monitoring its development to appropriately adapt its reporting processes and ensure compliance with future national and European regulatory frameworks.
5.2Climate adaptation, resilience and transition
Climate risks and opportunities
In the current context, Madrileña Red de Gas identifies and manages its climate-related risks and opportunities as a fundamental part of its corporate strategy. Understanding how climate change may affect its operations, supply chain, finances, or reputation enables the company to anticipate, adapt, and make informed decisions.
At the same time, identifying opportunities related to decarbonization, sustainable innovation, or energy efficiency can generate competitive advantages, access to green financing, and improved perception among its stakeholders. This identification not only responds to environmental demands but is also key to ensuring the long-term resilience and sustainability of the business.

To identify and manage its climate-related risks and opportunities, Madrileña Red de Gas relies on the recommendations of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures), which provide a structured and internationally recognized framework to integrate climate change into business strategy.
To evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities, two scenarios established by the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) have been considered:
High-emissions scenario: RCP 8.5 represents a pessimistic, high-emissions pathway in which no significant climate policies are implemented, fossil fuel use continues to grow, and global temperatures could increase by more than 4°C by the year 2100, leading to severe environmental and social impacts.
Low-emissions scenario: RCP 2.6 is an optimistic scenario that envisions a rapid and sustained reduction in emissions, aiming to limit global warming to between 1.5°C and 2.0°C. This scenario aligns with the goals of the Paris Agreement through the adoption of clean energy, energy efficiency measures, and carbon capture technologies.
Assessing risks and opportunities using different climate scenarios is essential, as it enables organizations to anticipate the potential impacts of climate change
Assessing risks and opportunities using different climate scenarios is essential, as it enables organizations to anticipate the potential impacts of climate change—both physical and transitional—on their operations, supply chains, and long-term strategies. By considering a range of scenarios, including those that assume limited warming, companies can identify vulnerabilities, adapt their business models, and uncover opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage.
Road to climate neutrality
To achieve European climate neutrality and reach a net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions balance by 2050, Madrileña Red de Gas has defined its own long-term strategy to reduce such emissions. The aim is to comply with the European-level reduction commitments as well as other EU objectives related to climate change.
Madrileña Red de Gas has defined its own long-term strategy to reduce such emissions. The aim is to comply with the European-level reduction commitments
For the previously described climate scenarios (RCP 8.5 and RCP 2.6), Madrileña Red de Gas has developed a GHG emissions reduction forecast towards the Net Zero target (Image 38), this is essential for a company to establish a climate strategy that is both coherent and science-based, particularly when taking into account the various climate scenarios proposed by the IPCC.
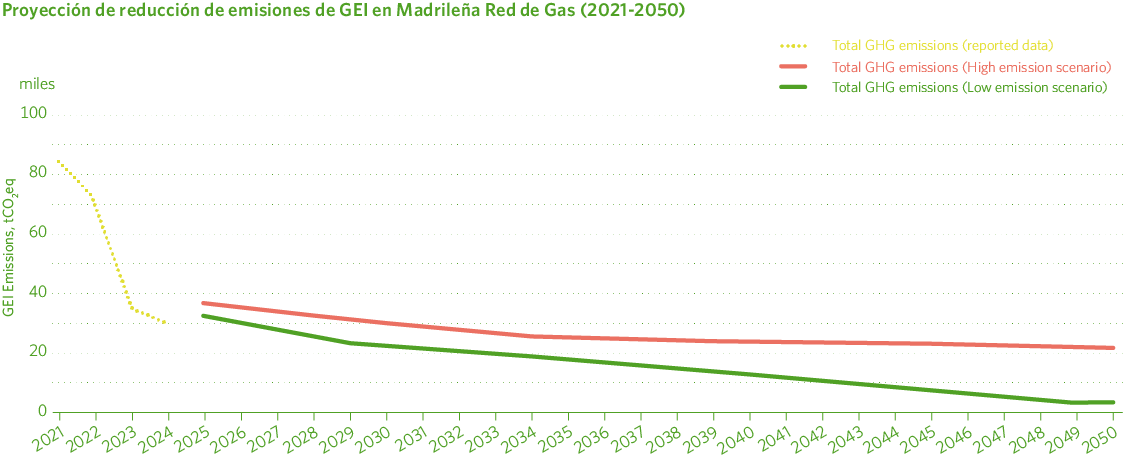
This forecast not only serves as a guide for investment and mitigation decisions, but also enables the company to anticipate risks, comply with emerging regulations, attract sustainable financing, and remain competitive in a market that increasingly values climate commitment.
Madrileña Red de Gas bases these projections on several factors, including the complete phase-out of the LPG business, the growth of the electric vehicle fleet, the replacement (or not) of natural gas with hydrogen, and the increasing share of energy from renewable sources, among others.
The foundation of this emissions reduction strategy is the annual measurement of the Carbon Footprint across Scopes 1, 2, and 3, together with a firm commitment to reduce it, as detailed in Chapter 8 of this report.
Additionally, a key pillar of the strategy focuses on the reduction of methane emissions, as shown below.
Methane emissions in gas distribution: a key challenge for sustainability
Methane, the main component of natural gas, is a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential more than 80 times greater than CO₂ over a 20-year time horizon. In the context of climate change, reducing methane emissions has become an international priority, as it represents one of the most effective and cost-efficient ways to mitigate short-term global warming.
In the context of climate change, reducing methane emissions has become an international priority, as it represents one of the most effective and cost-efficient ways to mitigate short-term global warming
Within the natural gas value chain, the distribution sector plays a key role. Although its emissions are typically lower than those from production or transmission segments, methane leaks in distribution networks constitute a significant source of diffuse emissions.
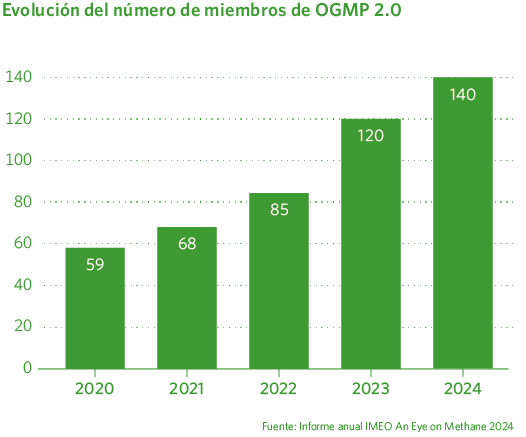
Against this backdrop, in 2023, Madrileña Red de Gas joined the OGMP (Oil and Gas Methane Partnership).
OGMP is an initiative led by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) through its Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC). Its main objective is to reduce methane emissions in the oil and gas sector. It promotes the transparent measurement, reporting, and reduction of methane emissions across the entire value chain, from production to distribution. In 2020, the OGMP 2.0 was launched—an enhanced version that sets the most rigorous international standard for the quantification and disclosure of methane emissions.
To date, more than 140 companies with assets across all five continents have joined the alliance, representing over 40% of global oil and gas production.
In line with OGMP objectives, Madrileña Red de Gas has committed to reducing its methane emissions by 10% by 2028
Madrileña Red de Gas participates in the biweekly meetings of the European distribution companies’ working group, where discussions focus on the guidance for achieving Level 5 “Gold Standard” certification, as well as on the harmonization of methane emissions quantification criteria.
Madrileña Red de Gas also took part in the technical meeting held in Utrecht in November, where studies conducted by the university were presented and data analyses from the distribution group were jointly reviewed.
In line with OGMP objectives, Madrileña Red de Gas has committed to reducing its methane emissions by 10% by 2028, using the levels reported in 2022 as a baseline. To meet this target, the company has established a six-year action plan (2023–2028) that includes concrete actions and milestones.
Under the current context, it is reasonable to assume that emissions could be slightly reduced through the implementation of the new European Regulation (EU) 2024/1787 on methane emissions reduction. This would be made possible by applying technologies identified as the most promising by technical consensus within OGMP 2.0 working groups, as well as by Marcogaz and Sedigas.
However, there is a risk that the deployment of new methane detection technologies and improvements in engineering-based calculations could uncover more gas leaks than are currently being identified. The International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO) has indicated that methane emissions detected via satellites are 90% higher than those reported by the industry.
As for the distinction awarded by OGMP 2.0, in 2024 Madrileña Red de Gas obtained the “Gold Standard Pathway” designation. This recognition reflects the company’s commitment to developing and implementing a robust, detailed, and credible action plan aimed at achieving the highest level of methane emissions monitoring within a three-year timeframe.
Driving the energy transition: Innovation and commitment to green energy
Decarbonising the economy—namely, the gradual elimination of fossil fuel use—is essential to achieving net-zero emissions. In this process, clean energy sources such as biomethane and hydrogen play a key role.
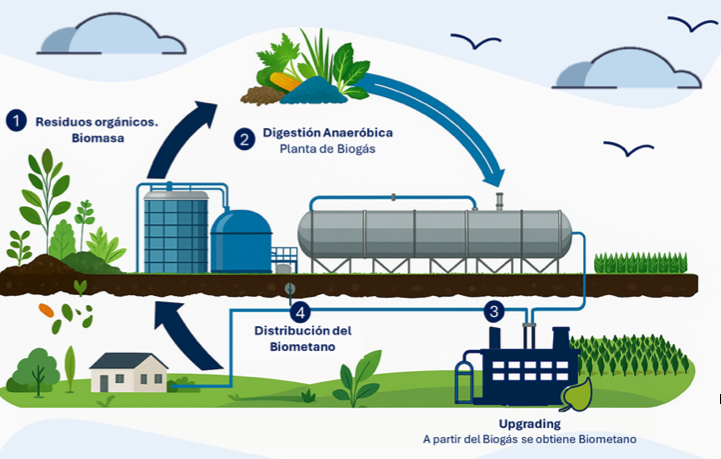
Biomethane is a renewable gas obtained through the purification of biogas, which is produced via the anaerobic digestion of organic waste (such as agricultural residues, manure, sewage sludge, or food waste). Its main advantage lies in its ability to be directly injected into existing gas networks and used in boilers, vehicles, or industrial processes without requiring major modifications.
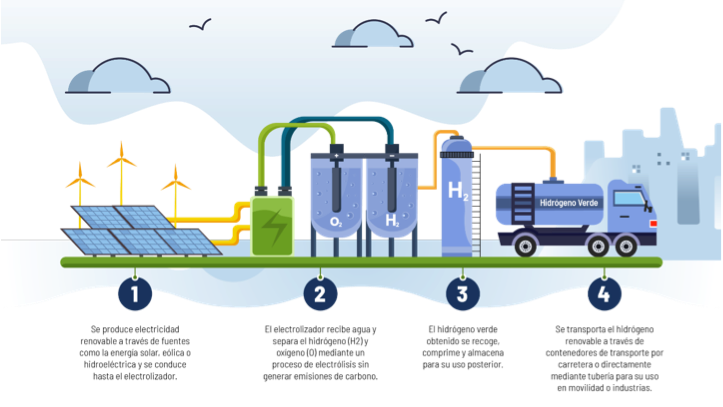
Green hydrogen, on the other hand, produced through water electrolysis using electricity from renewable sources, represents a key solution. As it does not emit CO₂ during its use and serves as a versatile energy carrier, hydrogen holds great potential to replace fossil fuels.
A Both energy vectors not only enable the reduction of direct emissions but also promote the circular economy, foster technological innovation, and strengthen energy security by reducing dependence on imported fossil resources. Their development is therefore a strategic commitment to meeting the climate goals of the Paris Agreement and ensuring a sustainable energy future.
biomethane and hydrogen are key pillars of the energy transition
In summary, biomethane and hydrogen are key pillars of the energy transition. Their gradual integration into current energy systems will allow for more robust progress towards a decarbonized, resilient, and just model, aligned with the net zero objective and the protection of the planet for future generations.
www.madrilena.es/nuevas-energias/
Show Room H2: Hydrogen use in Madrileña Red de Gas Facilities
With the aim of demonstrating the use of hydrogen as an energy source for heating and domestic hot water (DHW), in 2023 Madrileña Red de Gas signed an agreement with the boiler manufacturer Vaillant to install a prototype hydrogen-ready boiler.
This unit, the same size as its commercial natural gas equivalent, is capable of generating hot water from hydrogen. The boiler was installed in a room designated as a rest area for employees, providing both heating and hot water to the space. It is the first hydrogen boiler in operation in the Community of Madrid and the second in Spain.
The installation was assembled as if it were a natural gas boiler, following current regulations and using the same materials and installation procedures.
The boiler uses 100% hydrogen supplied from an external storage system, where, after a pressure regulation stage, the hydrogen arrives at the boiler at a pressure of 22 mbar. This demonstrates that current installations are capable of transporting hydrogen, opening the door to decarbonizing heating through the use of renewable hydrogen. Although it is not yet capable of using hydrogen-natural gas blends, the manufacturer is working in that direction.
During 2024, the installation has been visited by technicians from MITECO, representatives of the CNMC, associations such as CONAIF and AGREMIA, as well as various housing developers and installers.
Inspira Madrid project
Throughout 2024, the Inspira Madrid hydrogen generation project has continued to advance, developed as a consortium by three companies: Aliara Energía, Fotowatio Renewable Ventures Servicios España (FRV), and Grupo Ruiz.
Obtaining European funding
During 2023, efforts were focused on submitting Inspira Madrid to the funding call of the Connecting Europe Facility (CEF), specifically in the transport sector. This mechanism is a financial instrument created by the European Commission for the development of the Trans-European Network, emphasizing infrastructure for alternative fuels (AFIF).
After evaluating the proposals, the European Climate, Infrastructure and Environment Executive Agency (CINEA) selected 42 projects for the 2023 call, with a proposed support amounting to €424 million. Within this call, the EU’s CEF AFIF will support the construction of 4,200 electric charging points and 48 hydrogen refueling stations. Among the four Spanish projects selected by CEF AFIF, Inspira Madrid was the only one dedicated to hydrogen generation and refueling infrastructure in Spain.
Based on its fulfillment of priority and urgency criteria, maturity, quality, impact, and scalability, Inspira Madrid secured up to €7.3 million in European funds from the CEF Transport program
Based on its fulfillment of priority and urgency criteria, maturity, quality, impact, and scalability, Inspira Madrid secured up to €7.3 million in European funds from the CEF Transport program. Alongside the approval of additional financing from the Instituto de Crédito Oficial (ICO), the funding agreement with CINEA was signed mid-year, confirming the grant allocation.
Current status of the project
The support from the European Union through the granting of funds from the CEF program has propelled the project to advance into new development phases, beginning the preparation of the Advanced Basic Engineering stage prior to construction, together with Sacyr Proyecta. In parallel, work is ongoing with the Community of Madrid to advance the permits and environmental authorization for the hydrogen generation plant.
The correct location of hydrogen refueling stations is crucial for the project’s success, aiming to align demand with locations accessible from main communication routes
Likewise, the search for hydrogen consumers for mobility within the Community of Madrid is reflected in the numerous contacts and meetings held by the project development team. The correct location of hydrogen refueling stations is crucial for the project’s success, aiming to align demand with locations accessible from main communication routes.
Additionally, it is worth highlighting the strong collaboration between Inspira Madrid and the Toyota brand, in the form of agreements to facilitate access to hydrogen vehicles, specifically the Toyota Mirai. The agreement reached will provide a promotional discount on the vehicle price, bringing hydrogen mobility closer to the largest number of users during the project’s launch phase.
Pryconsa project
In 2022, an agreement was formalized between Pryconsa (Image 44), one of Spain’s leading housing developers, and Madrileña Red de Gas, with the objective of supplying hydrogen to a newly constructed building to meet heating and domestic hot water needs. This marks a significant step forward in decarbonizing the Spanish residential sector through the use of green hydrogen.
Construction of the housing development, where the hydrogen-ready boiler will be installed, began during 2024. The equipment to be installed will be a central boiler from the Bosch brand.
This boiler, the first of its kind installed in Spain, can be adapted to operate with different blends of hydrogen and natural gas. Starting from 100% natural gas, the boiler has the ability to modulate and operate with various mixtures of both gases, including the possibility to use 100% hydrogen and 100% biomethane.
Connected to the distribution network, the boiler will begin operation using natural gas and, being enabled for hydrogen use, will have the capacity to utilize green hydrogen when required.
Biomethane
During 2024, the CNMC resolution dated April 19, 2024, was published, establishing the procedure for managing connections of biomethane generation plants to the transmission or distribution network.
This procedure aims to manage the connections of biomethane generation plants to the natural gas transmission and distribution network. In compliance with this resolution, during 2024, Madrileña Red de Gas launched on its website a management tool for these requests. From the “new energies” section, users can find information about biomethane and hydrogen, request information for injecting renewable gases into the distribution network, and debunk biased and preconceived ideas surrounding hydrogen and biomethane, among other content.
In 2024, the first connection contract was signed for a production plant to inject biomethane into the Madrileña Red de Gas network
Additionally, in 2024, the first connection contract was signed for a production plant to inject biomethane into the Madrileña Red de Gas network. The biomethane production will come from a closed landfill in the municipality of Alcalá de Henares, where the landfill-generated biogas will undergo an upgrading process to inject the resulting biomethane into the network.
This milestone represents a first step in the decarbonization of the company’s distribution network, allowing biomethane to be delivered directly to current natural gas consumers. Injection of this renewable gas into the Madrileña Red de Gas network is expected to begin throughout 2026.
www.madrilena.es/inyectar-energia-a-la-red/
Collaboration with Universidad Francisco de Vitoria
Within the framework of the collaboration agreement established with Universidad Francisco de Vitoria (UFV), aimed at developing green hydrogen technology—from research to implementation and development—various actions have been carried out based on this objective.
Injection of this renewable gas into the Madrileña Red de Gas network is expected to begin throughout 2026
At the end of the year, a conference was organized for the engineering students of UFV. Addressing the challenges in distribution and supply for the energy transition, the event allowed sharing with future engineers the obstacles faced in hydrogen project development, the current state of the sector, and provided answers to their questions and concerns about this energy.
The successful participation and positive reception are proof of the interest future engineers have in green hydrogen, thereby reinforcing the activities carried out within the framework of the collaboration agreement.
In turn, this collaboration agreement has enabled two final-year engineering students from UFV to join Madrileña Red de Gas’s Expansion team as interns, supporting the department and allowing them to gain their first experience with biomethane and hydrogen projects
5.3Economic, financial and tax risk
Controlling economic, financial, and tax risks is essential for the stability and sustainability of Madrileña Red de Gas. Economic risks can affect profitability; financial risks jeopardize daily operations; and tax risks, arising from non-compliance with tax obligations, can lead to penalties and damage the company’s reputation.
Proper management of these risks allows Madrileña Red de Gas to anticipate problems, make informed decisions, and comply with legal obligations, which strengthens the company’s competitive position and ensures its long-term growth.
Controlling economic, financial, and tax risks is essential for the stability and sustainability of Madrileña Red de Gas
The economic, financial, and tax risks with the greatest impact on Madrileña Red de Gas during 2024, and therefore included in its corporate risk map, are the following:
- Tax inspections
This risk is based on possible cash outflows resulting from ongoing judicial and administrative procedures, as well as tax audits. The risk assessment considers the impact on cash flow if all open procedures are resolved unfavourably.Madrileña Red de Gas has hired a tax advisor to ensure proper technical support in tax matters. Currently, it awaits the corresponding judicial rulings, which will be decisive for the progress and definition of the course of actions to be taken.
- Natural gas demand and consumption variations
The demand risk is calculated based on the assumption that demand will remain at a certain level during the 2024–2032 period, i.e., until the end of the next regulatory period, considering that the decrease affects the residential sector.In this regard, Madrileña Red de Gas has a methodology to update projections annually based on the average demand of the last 10 years, through:
- Updating the connection points database with the latest forecast information.
- Updating the unit consumption of active connection points based on historical data from the last 10 years of the last closed year.
Based on the above, the projected demand has been updated using Madrileña Red de Gas’s historical data for the 2014–2023 period. Growth prospects remain as planned in the Business Plan approved in December 2023.
- Debt rating devaluation
The risk of debt rating devaluation refers to the possibility that rating agencies reduce the credit rating assigned to Madrileña Red de Gas, which can have significant financial repercussions. A downgrade usually leads to an increase in financing costs due to investors perceiving higher risk, as well as potential loss of market confidence, restricted access to credit, and negative effects on the value of issued debt instruments. It may also trigger unfavorable contractual clauses in previously signed financial agreements, affecting the company’s liquidity and stability.
Madrileña Red de Gas continuously adjusts and updates this risk based on the current context, calculating the percentage increase in financing cost over total debt if its rating were downgraded.
- Permanent gas balance losses
mainly due to gas theft and difficulties detecting faulty gas meters.The financial impact of this risk depends both on the volume of gas losses and the gas price. Since 2021, gas prices have shown an upward trend, with greater volatility and affected by a more unfavorable geopolitical scenario, making the impact of this risk high, even if gas losses decrease.
Since including this risk in the corporate risk map, Madrileña Red de Gas has made significant progress mitigating the impact through fraud detection campaigns, initially on the ground and also using IT tools to detect potential cases.
Furthermore, Madrileña Red de Gas’s annual financial audit plays a crucial role in risk management. By thoroughly reviewing its financial statements and internal controls, it helps identify vulnerable areas, irregularities, or possible deficiencies in accounting and operational processes that could represent financial, operational, or legal risks. Early detection of these threats helps prevent economic losses, regulatory sanctions, or reputational damage. Additionally, it provides Madrileña Red de Gas with a clear and objective view of existing risks, facilitating the implementation of more effective mitigation strategies.
5.4Cybersecurity
Information security and cybersecurity are fundamental pillars in modern companies, as they protect one of their most valuable assets: data. In an increasingly exposed digital environment full of threats and vulnerabilities, Madrileña Red de Gas ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, which is essential to maintaining the trust of its customers, shareholders, and employees.
Furthermore, proper cybersecurity management enables Madrileña Red de Gas to comply with legal obligations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), avoid financial penalties, mitigate reputational risks, and ensure business continuity in the face of cyberattacks or security incidents.
Investing in protective measures and awareness not only minimizes the impact of potential threats but also strengthens the resilience and competitiveness of companies in today’s market.
Information protection: a permanent priority
In 2024, Madrileña Red de Gas successfully completed the new certification cycle of its Information Security Management System (ISMS) in accordance with the international standard ISO/IEC 27001, thereby reinforcing its commitment to the security, confidentiality, and integrity of information. This certification has been fully integrated into the existing management system, enabling a unified view of processes and strengthening the organization’s culture of compliance.
The scope of the ISMS has also been expanded to include the personal data protection management model, thus consolidating a comprehensive security strategy that covers both corporate information and personal data.
Furthermore, the company has initiated the transition process to the new version of the standard, ISO/IEC 27001:2022. In this regard, revisions and updates have been carried out in the system documentation, as well as in the controls defined in the Statement of Applicability (SoA). These actions are currently in the evaluation and final adjustment phase, with the aim of ensuring proper alignment with the new regulatory requirements and maintaining the highest standards of information security management.
Analysis of Directive NIS2 (UE) 2022/2555
Although Madrileña Red de Gas has not been formally designated as critical infrastructure, it is actively working to comply with Directive (EU) 2022/2555 of the European Parliament and of the Council, dated 14 December 2022—commonly known as the NIS2 Directive—given the sectors it covers.
This regulation updates and replaces the previous NIS1 Directive with the aim of establishing a high common level of cybersecurity across the European Union, adapting to an increasingly complex and risk-exposed digital environment.
The study conducted represents the first step toward progressive alignment with the new regulatory framework and will serve as the foundation for defining an action plan to ensure effective implementation of the measures required by NIS2, in anticipation of its future transposition into national law. To this end, more than 100 relevant activities for the implementation of the directive have been analyzed, with an estimated compliance level of approximately 70%.
Personal data protection
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European law that governs the processing of personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). Its main objective is to strengthen individuals’ privacy rights and modernize data protection rules. The GDPR came into effect on May 25, 2018, and applies not only to organizations within the EU but also to those outside the EU that process data of individuals within the European territory.
Under the GDPR, there are two tiers of administrative sanctions depending on the severity of the violation. These can reach up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher, in the case of severe infringements.
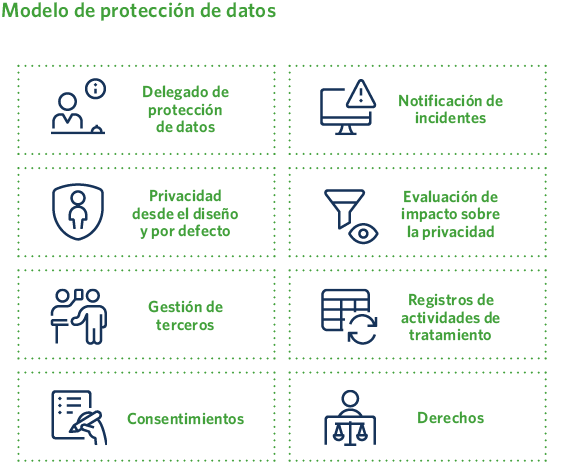
In compliance with the GDPR, Madrileña Red de Gas has implemented a robust data protection management model, through which it carries out all the necessary organizational, technical, and legal measures to ensure the protection of personal data.
As in previous years, in 2024 the company’s most significant personal data protection activities have primarily focused on managing data subject rights, handling incidents, and responding to queries—many of which are related to interpreting current legislation and facilitating the exercise of individuals’ data protection rights.
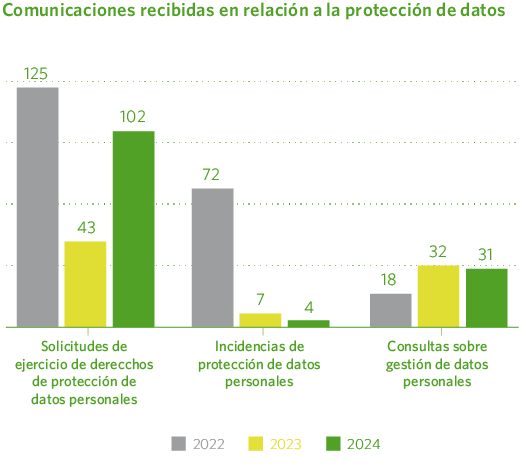
Throughout 2024, several communications concerning data protection were received and directed to the data protection officer.
In general, the data reflects an improvement in the management and protection of personal data, with fewer incidents and a more moderate demand for direct intervention by users—although interest in the subject remains high. This suggests that the measures implemented in recent years are proving effective.
Madrileña Red de Gas shield: comprehensive cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has gained increasing importance in recent years, becoming one of the most significant risks in 2024. As previously noted, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has included the risk of cyberattacks in its Top 10 global risks since 2018, and it continues to rank as one of the most likely and high-impact threats to date.
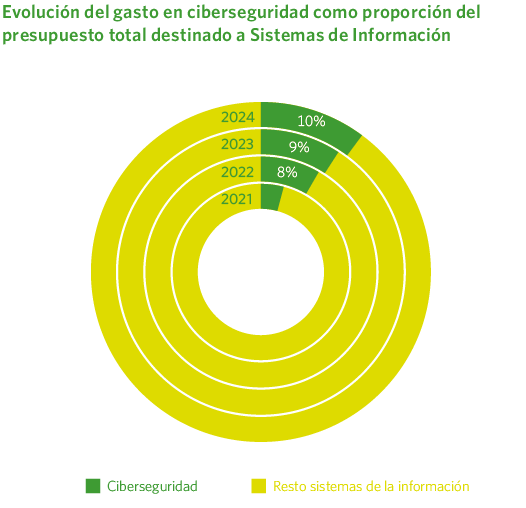
Madrileña Red de Gas considers cybersecurity a key pillar of its corporate strategy. In response to the new challenges posed by digitalization, open data management, the use of cloud technologies, and the need to protect its operations, the company intensified its cybersecurity efforts in 2024. These actions have strengthened its ability to prevent, detect, and respond to digital threats.
In this context, cybersecurity investment in 2024 accounted for 10% of the company’s total Information Systems expenditure, reflecting the growing strategic importance of protecting digital assets and ensuring operational continuity in the face of cyber threats.
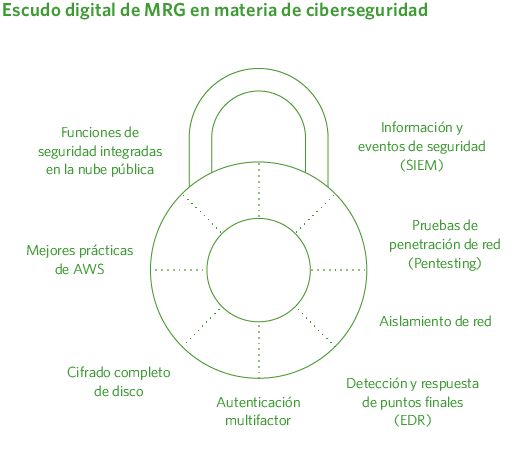
Madrileña Red de Gas has established a true digital “shield” within the company, designed to analyze, detect, and prevent potential cyberattacks that could compromise the various systems used in its operations.
Contingency management and technological resilience at Madrileña Red de Gas
Backup Policyç
At Madrileña Red de Gas, backup policies are essential to protect data and ensure its recovery in case of loss. The company has defined which data must be backed up and at what frequency.
Currently, different types of backups are performed depending on whether it is a system backup or a database backup. Additionally, a third backup of SAP data is made on a separate account and in a different AWS region for added security.
Business Continuity Plan
The objective of this plan is to recover the company’s productive capacity while ensuring compliance with regulations following any disruption caused by a cyber incident.
It is reviewed annually in collaboration with the various business units.
Disaster Recovery Plan
A disaster recovery plan is established for each of the company’s critical systems.
Annual disaster recovery drills are conducted to guarantee the proper functioning and readiness of these systems.
Cybersecurity Insurance Policy
The cyber insurance contracted with a specialized company helps cover costs associated with the coverage and provides legal and technical support to facilitate recovery as soon as possible after a security incident. However, it does not prevent the company from experiencing cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity master plan 2024-2026
The Madrileña Red de Gas Cybersecurity Master Plan 2024-2026 establishes a clear and structured strategy to protect its digital assets, ensure business continuity, and minimize risks against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats
The Madrileña Red de Gas Cybersecurity Master Plan 2024-2026 establishes a clear and structured strategy to protect its digital assets, ensure business continuity, and minimize risks against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. It aligns cybersecurity with corporate objectives, facilitating informed decision-making and efficient resource allocation. Furthermore, it contributes to regulatory compliance and enhances the confidence of customers and shareholders by demonstrating a serious commitment to information protection.
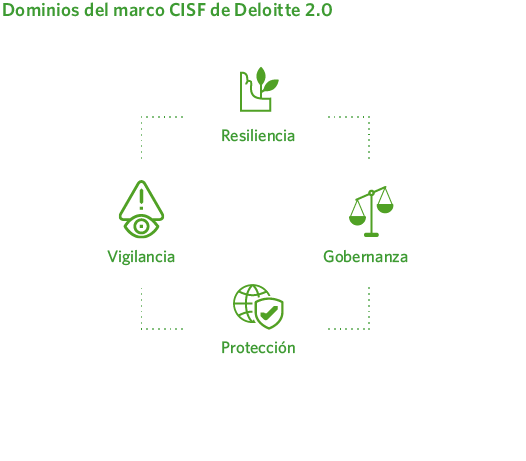
Madrileña Red de Gas with the goal of progressively increasing the maturity level in this area. The plan is organized according to a prioritization criterion, divided into three successive waves over the specified period. Each of these waves includes projects distributed across the four domains defined by Deloitte’s CISF framework version 2.0.
In 2024, the first wave of the plan has been completed, completing eight key initiatives that have allowed to strengthen the security stance of the company.
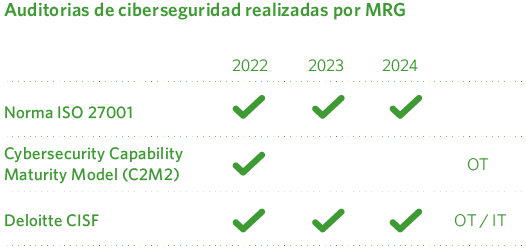
Cybersecurity audits
Audits are a fundamental component in managing information security and technological infrastructure within a company. In this context, Madrileña Red de Gas conducts audits in key areas such as information security (audits according to ISO 27001), information technology (IT audits), and operational technology (OT audits). These audits have become essential to identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and ensure that the organization operates efficiently and securely.
These audits enable Madrileña Red de Gas to:
- Evaluate its cybersecurity maturity level according to Deloitte’s Cyber Industrial Strategy Framework (CISF) v2.0.
- Perform a benchmarking analysis of the company’s current position within the sector.
- Identify the target maturity level, strengths, and opportunities for improvement.
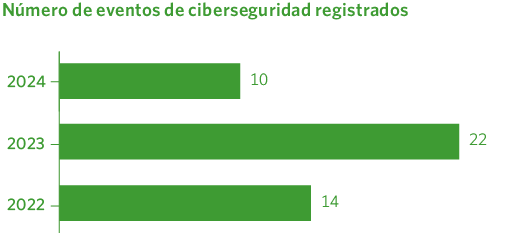
Monitoring: evolution of cybersecurity events
Madrileña Red de Gas maintains rigorous and continuous monitoring of all cybersecurity-related events, enabling it to assess trends, anticipate potential threats, and continuously improve its defenses. During 2024, there was a decrease in the number of detected events compared to previous years.
This decrease is a positive sign that reflects both the effectiveness of the preventive measures implemented and the growing commitment of the teams to good digital security practices.
Improvements in training, the use of more advanced tools, and greater overall awareness have contributed to significantly reducing events, thereby strengthening Madrileña Red de Gas’s stance against cyber risks.
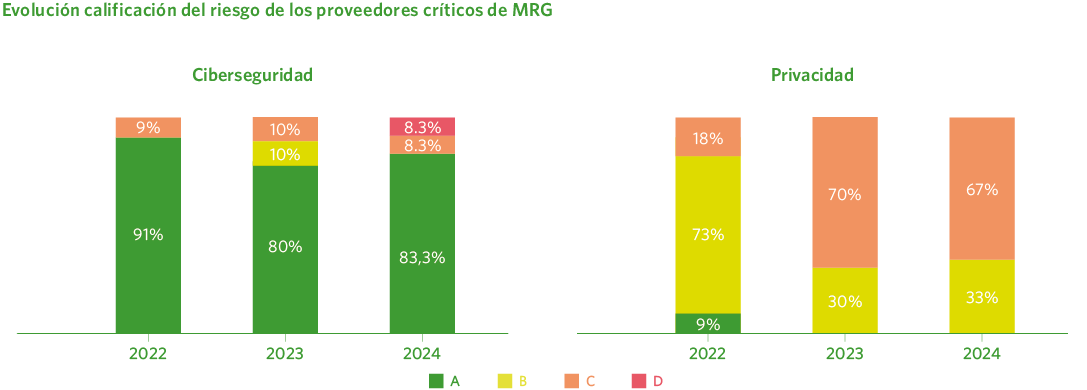
Control and security in the supply chain
Madrileña Red de Gas, as detailed in Chapter 7 on the Supply Chain of this report, collaborates with a large number of suppliers and contractors for the execution of various services and activities, such as operations, development, maintenance, among others.
Through the Information Security Policy in Supplier Management, Madrileña Red de Gas establishes the principles and commitments that suppliers must comply with regarding the handling of information during the execution of their activities.
Madrileña Red de Gas integrates various mechanisms in its management model to ensure information security and data protection in its relationship with suppliers
Madrileña Red de Gas integrates various mechanisms in its management model to ensure information security and data protection in its relationship with suppliers. These include specific contractual clauses, confidentiality agreements, a purchasing portal for operational management, identification of critical suppliers in terms of security, as well as coordinated actions with data processors.
Furthermore, the risk analysis carried out through the supplier prequalification tool allows evaluating the current status of suppliers based on a set of relevant regulatory frameworks, presenting the results through a legal rating. This analysis mainly focuses on aspects related to privacy and cybersecurity, assessing the existing risk from both perspectives.
Throughout 2024, the vast majority of Madrileña Red de Gas’s critical suppliers (see Chapter 7 for more information on critical suppliers) were evaluated according to the previously mentioned criteria .
Collaborative cybersecurity: together against threats
Since 2022, Madrileña Red de Gas has maintained active collaboration with the National Cybersecurity Institute (INCIBE) through the subscription to various strategic services aimed at prevention, detection, and response to digital threats. This cooperation has strengthened its capabilities in cybersecurity protection and risk management and is structured through the following services:
- Early warning service for new vulnerabilities detected at the national and international levels.
- Information exchange on cyber threats, facilitating a coordinated and effective response.
- Access to specialized technical cybersecurity content, enabling continuous training and updating of teams.
- Proactive detection of threats and risks in systems and networks.
- Assistance in responding to security incidents that may compromise the integrity of information or critical services.
As part of this collaboration, a permanent channel for technical information exchange has been established, complemented by participation in regular meetings and sector events organized by INCIBE. Notably, Madrileña Red de Gas participated in the International Information Security Meeting (ENISE), held in León from October 21 to 23, 2024, a key forum for promoting knowledge and cooperation in cybersecurity.
Additionally, discussions have begun to carry out cyber exercises to evaluate and strengthen Madrileña Red de Gas’s response capacity to cybersecurity incidents from both technical and organizational perspectives. These exercises also aim to improve coordination with public bodies and partner entities, thereby consolidating a comprehensive strategy for prevention and digital resilience.
5.5Asset integrity and critical accident management
For Madrileña Red de Gas, as a gas distribution company, the integrity of its assets, as well as the prevention and management of incidents and accidents that could seriously harm health, the environment, and the economy, are clearly material issues.
Moreover, the nature of the business entails a mandatory compliance with national and regional legislation designed to ensure safety around installations and for the workers themselves. In this regard:
- The gas distribution pipeline network is required to implement emergency measures as established in Article 20 of Law 31/1995 on Occupational Risk Prevention and section 6.2 of point 6 of ITC-ICG 01, “Installations for the distribution of gaseous fuels through pipelines,” under Royal Decree 919/2006 (Technical Regulation on the Distribution and Use of Gaseous Fuels and its complementary technical instructions).
- Royal Decree 393/2007, of March 23, establishes the Basic Self-Protection Standard for centers, facilities, and premises dedicated to activities that may give rise to emergency situations.
- Furthermore, although the goal is to eliminate LPG plants through conversion to natural gas, in 2024 Madrileña Red de Gas still operated three LPG plants subject to the SEVESO III Directive.
The company has documented and consistently maintained up-to-date management systems necessary for risk identification, prevention, and emergency response, in accordance with various UNE-EN ISO Management System standards and regulatory requirements.
Among the key initiatives carried out in 2024, it is worth highlighting the development and implementation of the Self-Protection Plan for the LNG Plant in Miraflores de la Sierra (Image 57). This facility includes an 80 m³ storage tank and is therefore subject to Royal Decree R.D. 393/2007. The plant is located on the same site where the former Los Lagunazos LPG plant once stood. The new LNG facility features significantly more advanced technology and safety measures compared to the installation it replaces.
In 2024, within the scope of SEVESO-affected assets, Madrileña Red de Gas undertook a revision of its Internal Emergency Plans, introducing modifications to align their contents with the overall self-protection and emergency management model. Specifically, two Internal Emergency Plans were revised, successfully passing evaluation by the Authorized Control Body (OCA) in 2024. These plans were subsequently submitted to the Regional Government of Madrid in 2025.
Both LPG plants are scheduled for dismantling, in line with the company’s objective to phase out this type of facility—contributing to enhanced safety and reduced emissions. The revised plans were as follows:
- Zarzaquemada Complex: This facility has already been decommissioned and inerted, beginning the dismantling process. Located relatively close to the urban core of Leganés, its removal significantly reduces the risk component for nearby residents.
- Villanueva de la Cañada: This site includes two LPG plants, one of which falls under SEVESO regulations. The conversion from LPG supply points to natural gas is already underway in the municipality and is expected to be completed in 2025. Upon completion, both facilities will be inerted and dismantled.
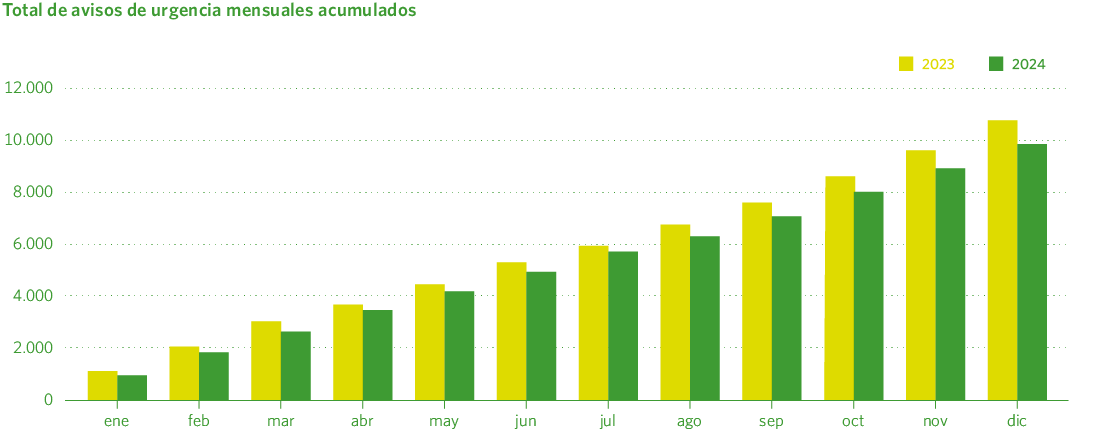
Emergency response 2024
Madrileña Red de Gas’s Emergency Control and Assistance Center (CCAU) is equipped with the necessary human and material resources to receive all emergency alerts and communicate them quickly, clearly, and reliably to the response teams, operating 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Through this service, a total of 48,283 calls were managed by the Call Center in 2024, representing a 17% decrease compared to the previous year. Additionally, 9,889 emergency alerts were generated and attended to, marking a 7.9% reduction from 2023.
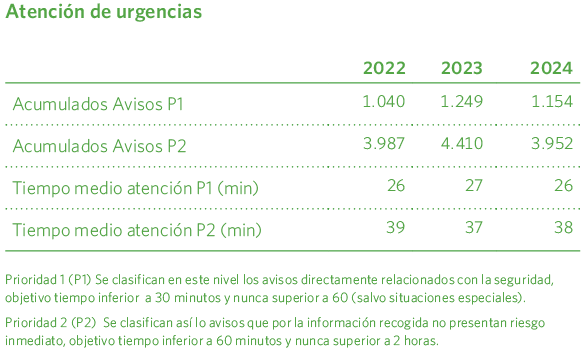
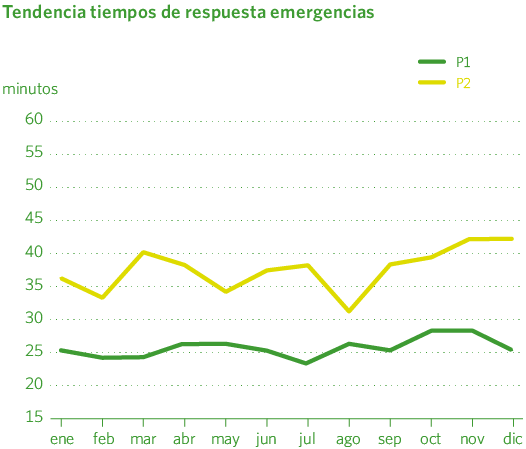
The notification of an emergency to the chain of command of the affected technical services is always carried out as indicated in the Emergency Plan. The CCAU has a telephone system for handling emergencies, with calls recorded for a period of two months. The emergency response teams possess the technical and operational knowledge required to ensure proper action, both in the work carried out on transport and distribution networks, and in receiving installations, as well as the occupational risk prevention specifications related to these actions. The priority of an alert is determined based on the level of risk that can be initially inferred from the information collected during the call. This is established on five levels: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, ranging from immediate action to scheduled intervention, depending on the level of risk or urgency.
This year, 3,952 Priority 2 alerts were received, with an average response time of 38 minutes. There were 1,154 Priority 1 alerts, responded to in an average of 26 minutes, with a 99.3% compliance rate within less than one hour, significantly exceeding the quality target of 30 minutes with 96% within an hour.
The average response time was 31 minutes, eight minutes less than last year. The volume of gas released reached 1.05 GWh, with costs recovered in almost all cases.
Subsequently, we always conduct a results analysis and prepare Emergency Reports. This analysis allows us to evaluate response times and operations, and helps identify opportunities for improvement. In addition to these reports, periodic reports are issued with analyses of weekly and monthly emergency response activities, calculating metrics that allow for the evaluation of service quality.
Within the Emergency department, 72 cases of fraud/manipulation related to emergency calls have been detected.
As every year, all necessary equipment and tools for emergency operations have been kept in perfect condition, calibrated, and inspected.
Emergencies and autoprotection
It is important to highlight the training carried out in 2024 regarding emergency plans at the facilities. During the summer of 2024, new training sessions were held on the emergency plans for the satellite LPG plants, while by the end of the year, additional training focused on the emergency plans for the distribution network.
In the last quarter of 2024, an awareness campaign was conducted on the emergency plans for both the Pozuelo center and the warehouse. Drills were carried out at both work sites, during which potential areas for improvement were identified and documented in the corresponding drill reports for further action.
